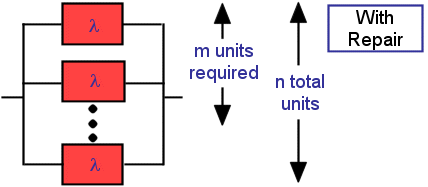
This tool calculates the effective failure rate of "n" active online units, where "m" are required for successful operation. The calculation implements Equation 1 shown on page 90 of the United States Air Force Rome Laboratory Reliability Engineer's Toolkit (1993). It takes into account repair of any failed units and assumes that these units are repaired within the mean corrective maintenance time (Mct) entered below. See this page for additional details on time inputs (Mct) for system restoration. The effective mean time between failure (MTBF), sometimes referred to as the mean time between critical failure (MTBCF), is the reciprocal of the effective failure rate.