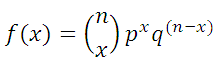
The tool also calculates the cumulative probability that not more than r failures will occur in a sample of n items. The cumulative probability that r or fewer failures will occur in a sample of n items is given by:
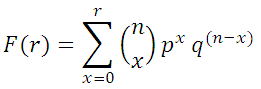
where q = 1 - p.
For example, a manufacturing process creates defects at a rate of 2.5% (p=0.025). A sample of 20 parts is randomly selected (n=20). What is the probability that the sample contains 3 or fewer defective parts (r=3)? The probability of finding 3 or fewer defects in 20 samples is 0.9986.

